News and Events
The company
Itaipu Binacional is the result of a partnership between the governments of Brazil and Paraguay. The company started in 1974. Its mission was to build and operate the Itaipu hydropower plant, the largest in the world by then.
The plant is located at the Paraná River, the border between the two countries. It is the single plant that has generated the most energy in history, with more than 3.1 billion Megawatt-hours since it started operating, in 1984.
But the company does not only generate electricity. Since its inception, Itaipu Binacional has followed sustainable development principles as reflected by its integrated environmental, social, and economic initiatives that promote prosperity in both countries.




-
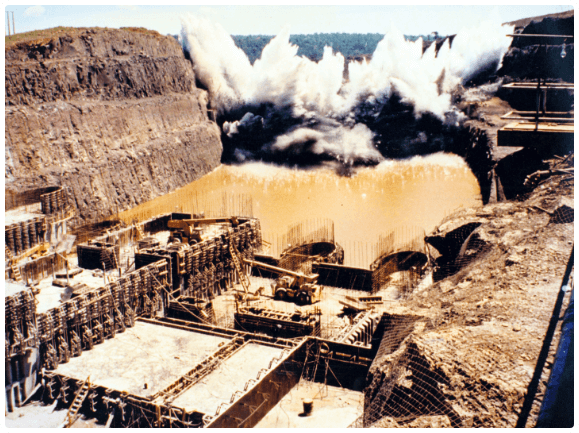
The construction
The dam’s construction took place from 1975 to 1982 and employed 40,000 Brazilian and Paraguayan workers at its peak. The dam’s conclusion allowed the formation of the reservoir, and Itaipu kick-started the operation Mymba Kuera, which rescued more than 36,000 wild animals.
Then, the assembling of electro-mechanical parts started. By 1992, the plant was already operating the first 18 generating units conceived on the original blueprint. Two more units were added in 2007 and the plant reached its full capacity, with 20 units of 700 Megawatts each.
![The construction]()
![The construction 2]()
![The construction 2]()
![The Construction]()
-
Legal nature
Itaipu is an international entity directly created by the Treaty between Brazil and Paraguay on April 26, 1973. Previously, both countries had already signed the Act of Iguaçú, agreeing to explore the Paraná River to generate hydropower, cooperatively.
That’s why Itaipu is not only the result of civil and electrical engineering, but also viewed as a diplomatic achievement that solved border disputes between Brazil and Paraguay that had been discussed for over a century.
Therefore, Itaipu is considered a benchmark for international partnerships, for it peacefully ended border issues and, at the same time, generated economic, social, and environmental benefits for two nations.
-
Mission
To generate quality electrical energy via socially and environmentally responsible practices, fostering sustainable development in Brazil and Paraguay.
-
Vision
To be a modern binational entity, collaborative and committed to regional integration, recognized for its excellence in generating clean and renewable energy and for its contribution to the sustainable development of Paraguay and Brazil.
-
Supervisory Board and Directors Board
The governments of Brazil and Paraguay are responsible for appointing the Itaipu Binacional Executive Board of Directors. Each position allotted to a country has its counterpart on the opposite side.
In addition to the Executive Board of Directors, Itaipu has a Supervisory Board with twelve members, six from Brazil and six from Paraguay, and one representative from each country’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
-
Financial statements
Here you can find the Annual Financial Statements of Itaipu Binacional.
Just click on the year to open the file in PDF format.
The powerplant
Itaipu is a world leader in the production of clean and renewable energy
The hydropower plant belongs equally to Brazil and Paraguay, and each country owns half of the electricity produced.
There are 20 generating units of 700 Megawatts each, which comprise 14,000 Megawatts of installed capacity. Ten units operate in 50 Hertz, the utility frequency in Paraguay. The other 10 operate in 60 Hertz, the frequency used in Brazil.
Itaipu provides around 90% of the electricity consumed in Paraguay and 10% in Brazil. It is the single plant that has produced the most energy in history: more than 3 million Gigawatt-hours since 1984, enough to supply the world for 43 days.
Since 2012, the plant has had a management system designed to improve its efficiency by making the most of all water that reaches the reservoir.
103,100 GWh
Best annual output (2016)
20
Generating units
83,800 GWh
Annual output (2023)
7.9 Km
Length of the dam
14 GW
Installed capacity
196 m
Maximum height of the dam
The reservoir
Itaipu’s reservoir extends for 170 km along the Paraná River, the border between Brazil and Paraguay
The artificial lake serves multiple uses besides energy generation, such as water supply, agriculture, fish production, tourism, and wildlife conservation.
Itaipu promotes a series of initiatives that aim to ensure the quantity and quality of water in the reservoir in the long term. One of the main ones is the conservation of 100 thousand hectares of the Atlantic Forest that surround it, in both margins.
This green infrastructure – designated as Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO – provides various ecosystem services, including benefits for food production, one of the main economic activities in the nearby territory. Itaipu also promotes the recovery of nearby watersheds in partnership with municipalities and the communities.
1,350 km²
Water surface
29
billion m³
Volume of water
100,000 ha
Protected forests
5.9
million Tons
Of CO2 annual fixation by forest biomass
500
Micro watersheds recovered
42
Stations of environmental monitoring
Sustainability
Environmental care and social responsibility are essential commitments linked to Itaipu’s strategic planning
The company’s mission highlights the importance of sustainable development as the sine qua non of clean and renewable energy generation for Brazil and Paraguay.
These commitments translated into policies and practices that promote ecosystems conservation and the well-being of the population. In Brazil, these actions take place in the western region of Paraná, and Mato Grosso do Sul states. In Paraguay, they have national coverage and benefit different regions of the country.
Within the social dimension of sustainable development, activities by Itaipu are designed to help to reduce poverty, increase food security, nutrition, and health, foster better education, and promote income. The company also acts on promoting tourism and improving the infrastructure at the border region.
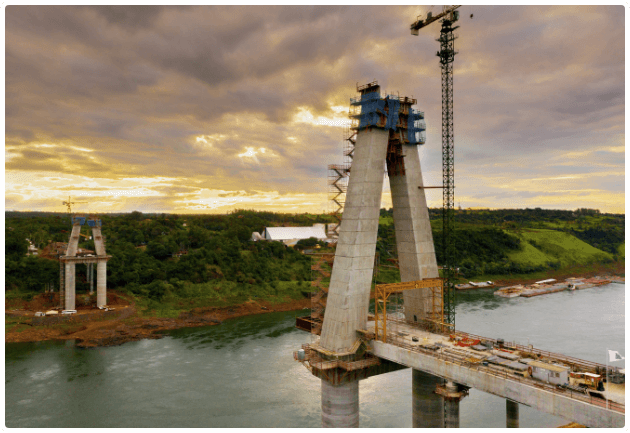




2
New bridges between Brazil and Paraguay
24 million
Visitors to Itaipu since 1977
10,000
Families of farmers assisted
2
Public hospitals supported
300
Programs benefitting indigenous communities
2,000 km
Of rural road improvements
The 2030 Agenda


Itaipu partnered with the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) to promote water and energy sustainably. One of the results is the Sustainable Water and Energy Solutions Network, a multi-stakeholder initiative with organizations from around the world to promote an integrated approach to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 6 (water) and 7 (energy) and their interlinkages with the other SDGs that are part of the 2030 Agenda.
As a technical product of this partnership, Itaipu published 17 case studies responding to the 17 SDGs. This collection offers a broad view of Itaipu’s contribution to sustainable development in Brazil and Paraguay. Not only with the generation of clean and renewable energy but also with environmental and social initiatives. It’s also possible to download a synthesis report with the main actions related to each SDG.
Itaipu’s 17 Case Studies Responding to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals
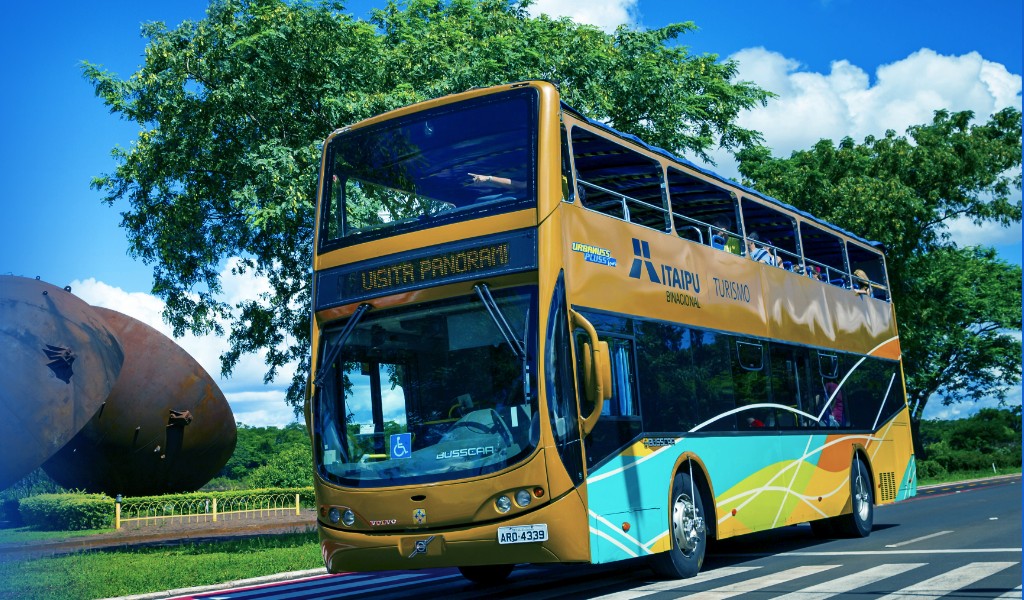
Visit Itaipu
The border between Brazil and Paraguay has several tourist attractions, including natural wonders, such as the Iguaçu and the Monday falls.
Aware of the region’s potential, Itaipu promotes a series of initiatives to attract tourists worldwide and to enhance the quality of local infrastructure and services. The promotion of tourism is also part of Itaipu’s mission as a way for the company to promote the economy sustainably.
And Itaipu is a tourist attraction itself, offering different options of tours in both margins.
Click here to visit Itaipu in the Brazilian margin→ Click here to visit Itaipu in the Paraguayan margin→For institutional visits, such as universities, governments, and other organizations, see the contact info session at the bottom of the page.
Visit Itaipu
The border between Brazil and Paraguay has several tourist attractions, including natural wonders, such as the Iguaçu and the Monday falls.
Aware of the region’s potential, Itaipu promotes a series of initiatives to attract tourists worldwide and to enhance the quality of local infrastructure and services. The promotion of tourism is also part of Itaipu’s mission as a way for the company to promote the economy sustainably.
And Itaipu is a tourist attraction itself, offering different options of tours in both margins.
Click here to visit Itaipu in the Brazilian margin→ Click here to visit Itaipu in the Paraguayan margin→For institutional visits, such as universities, governments, and other organizations, see the contact info session at the bottom of the page.